贝塞尔曲线推导以及python代码实现
原理

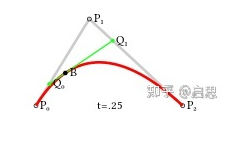
保持比例不变
 不断运动,最后
不断运动,最后

拓展到高阶
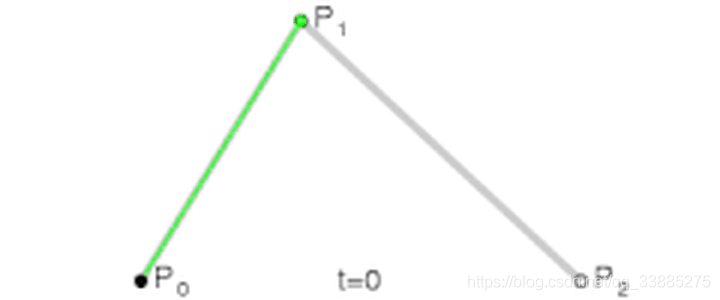
不断两两连线
n阶可以变成n-1阶。
从而不断递推到0阶(也就是说只有一个点)
在不断变化过程,保持各线段的比例相等。
运动的变量也是比例rate,从[0,1]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
from matplotlib import pyplot
import numpy as np
points = [
[0,0],
[1,0],
[1, 1],
[2,1]
]
points = np.array(points)
# 通过递归构造贝塞尔曲线
def calNextPoints(points, rate): # 如果给定了具体的n, 那么可以直接得到计算方程
if len(points) == 1:
return points
left = points[0]
ans = []
for i in range(1, len(points)): # 根据比例计算当前的点的坐标,一层层的推进
right = points[i]
disX = right[0] - left[0]
disY = right[1] - left[1]
nowX = left[0] + disX * rate
nowY = left[1] + disY * rate
ans.append([nowX, nowY])
# 更新left
left = right
return calNextPoints(ans, rate)
X= []
Y = []
for r in range(1, 100):
r = r / 100
a = calNextPoints(points, rate=r)
# print(a)
x = a[0][0]
y = a[0][1]
X.append(x)
Y.append(y)
print(points[:,1])
pyplot.scatter(points[:,0], points[:,1], c='blue')
pyplot.plot(X, Y)
pyplot.show()
|
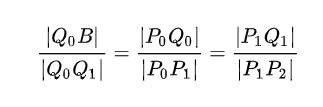 不断运动,最后
不断运动,最后

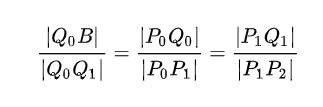 不断运动,最后
不断运动,最后
