pandas
行列
1
2
3
4
5
|
# 获取某一列
data['key']
# 获取多列
data[['key1', 'key2']]
|
数据条件筛选
通过[]进行基本的行筛选
1
2
3
4
5
|
# 筛选出key属性等于1的所有行,也可以用>,< 以及用&等逻辑组合
data[data['key'] == 1]
# 筛选出前100行
data[0:100]
|
通过loc以及iloc进行行以及列的筛选
- loc按标签值(列名和行索引取值)访问,
- iloc按数字索引访问
首先loc
1
2
3
4
5
|
# 基本[]支持的loc也都支持
data.loc[data['key'] == 1]
# 同时还支持列的筛选, 列用:同样可以视作全选
data.loc[0:100, ['key1', 'key2']]
|
然后iloc
1
2
|
# 筛选出前100行,前1,2列
data.iloc[0:100, [0,1]]
|
关于字符串匹配value
1
2
|
# 下面利用titanic的数据举例,筛选出人名中包含Mrs或者Lily的数据,|或逻辑符号在引号内。
train.loc[train['Name'].str.contains('Mrs|Lily'),:].head()
|
- case=True:使用case指定区分大小写
- na=True:就表示把有NAN的转换为布尔值True
- flags=re.IGNORECASE:标志传递到re模块,例如re.IGNORECASE
- regex=True:regex :如果为True,则假定第一个字符串是正则表达式,否则还是字符串
逐行进行遍历
1
2
3
|
# values 是负责把值取出来
for row in CRAN_data.iterrows():
print(row[1].values)
|
查看某一列的特征:平均值,count统计,max,min,std方差
1
2
3
4
|
data_projects["Platform"].unique() # 查看共有多少中可能的取值
data_projects["Platform"].value_counts() # 同个各个离散变量的个数
data_projects["Platform"].min()
# 以及mean(), max(),
|
**dataF.describe()**可以一次性查看表的各项属性的特征
numpy
关于reshape
快速改变向量的shape。但是并不会改变原始的顺序。
也就说说,如果按照从里到外的遍历顺序,那么无论怎么reshape的顺序是不会变的。
初期数据及库准备:
import numpy as np # 调用numpy库
设置一个1-18的列表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
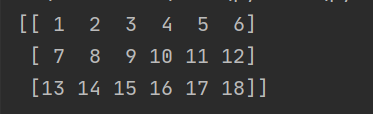
anchors = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18]
#将anchors由列表转换为数组的形式
anchors = np.array(anchors)
一维reshape() 为 二维
18个元素一维度数组,可以转换为2 x 9 及 3 X 6的二维数组
print(anchors.reshape([3,6])) # 生成一个(3,6)的二维数组
print(anchors.reshape([2,9])) # 生成一个(2,9)的二维数组
|


关于计算
可以直接做逻辑运算。
1
2
|
num = np.array([0,1,2,1,0,1,0])
num == 1
|
1
|
array([False, True, False, True, False, True, False])
|
可以直接做算数运算
1
2
|
num = np.array([0,1,2,1,0,1,0])
num*2
|
1
|
array([0, 2, 4, 2, 0, 2, 0])
|
条件选择数据
先获取索引,通过where函数
1
2
3
|
num = np.array([0,1,2,1,0,1,0])
np.where(num == 1)
|
然后可以通过index,筛选数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
num = np.array([0,1,2,1,0,1,0])
index = np.where(num == 1)
index, num[index]
out:
((array([1, 3, 5]),), array([1, 1, 1]))
|
关于随机选择数据
同上,只不过把index的获取变成随机。
1
2
3
4
5
|
import random
def getRandomIndex(n, x):
# 索引范围为[0, n), 随机选x个不重复
index = random.sample(range(n), x)
return index
|
将数据打乱
同样也可以用index,因为index可以打算顺序。所以可以用这张方式来讲数据打乱
pytorch
Pytorch之permute函数, 变换维度的重要函数
在lstm中,我们的数据通常是,batch, seq, dim。
但是要求输入却是:seq, batch, dim
所以需要做数据变换,但是传统的reshape,和view并不能改变数据的底层排列顺序。
这种时候就需要用到permute函数。
Tensor.permute(a,b,c,d, …):permute函数可以对任意高维矩阵进行转置,但没有 torch.permute() 这个调用方式, 只能 Tensor.permute():
(abcd)是index,个人可以理解为改变检索方式
1
2
3
4
5
|
a = tensor[a][b][c]
b = a.permute(2,1,0)
那么相当于吧检索的顺序改变一下。
也就是说会有:
a[A][B][C] = b[C][A][B]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import torch
import numpy as np
a=np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]])
unpermuted=torch.tensor(a)
print(unpermuted.size()) # ——> torch.Size([1, 2, 3])
permuted=unpermuted.permute(2,0,1)
print(permuted.size()) # ——> torch.Size([3, 1, 2])
view_test = unpermuted.view(1,3,2)
print(view_test.size())
|
乘法
Torch.mm(): 对两个二维矩阵做矩阵的乘法
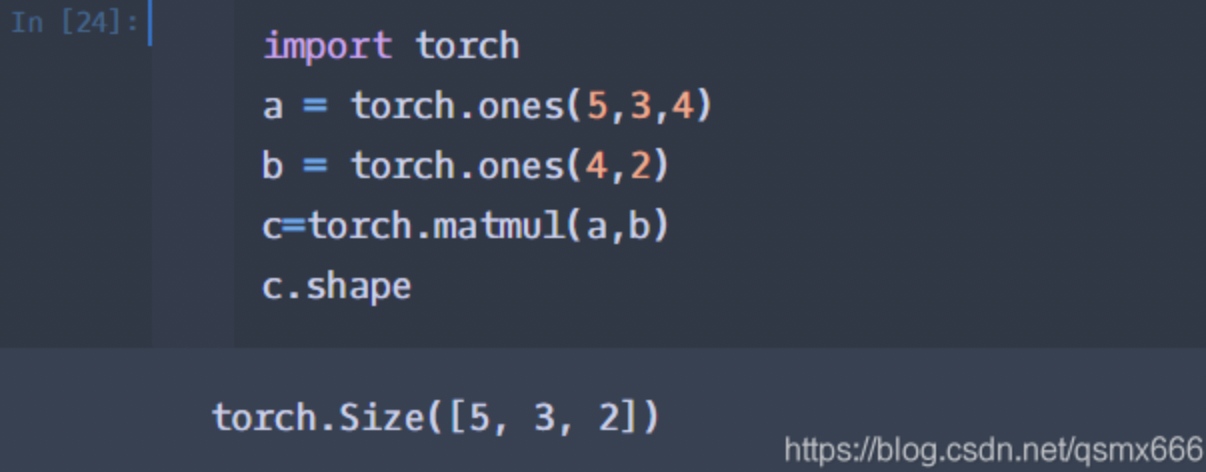
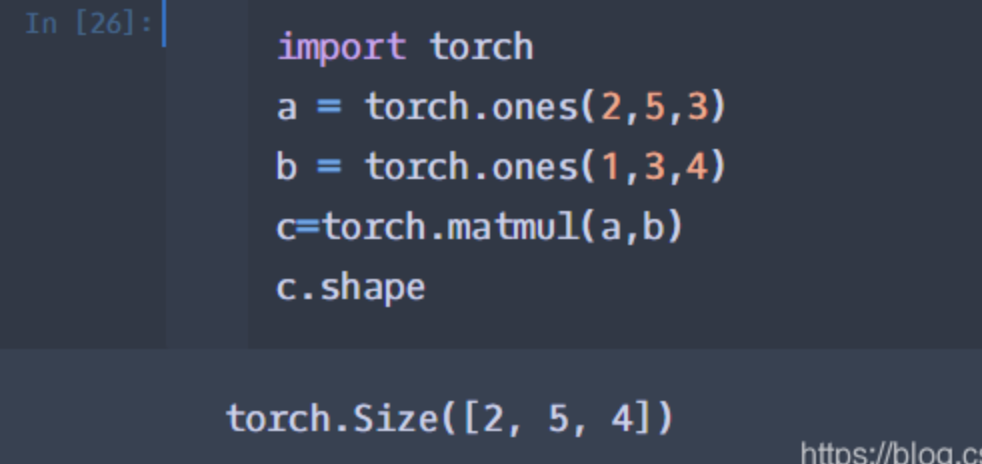
Torch.matmul():输入可以是高维的。
当输入是都是二维时,就是普通的矩阵乘法,和tensor.mm函数用法相同。
当输入有多维时,把多出的一维作为batch提出来,其他部分做矩阵乘法。

或者都是3维的