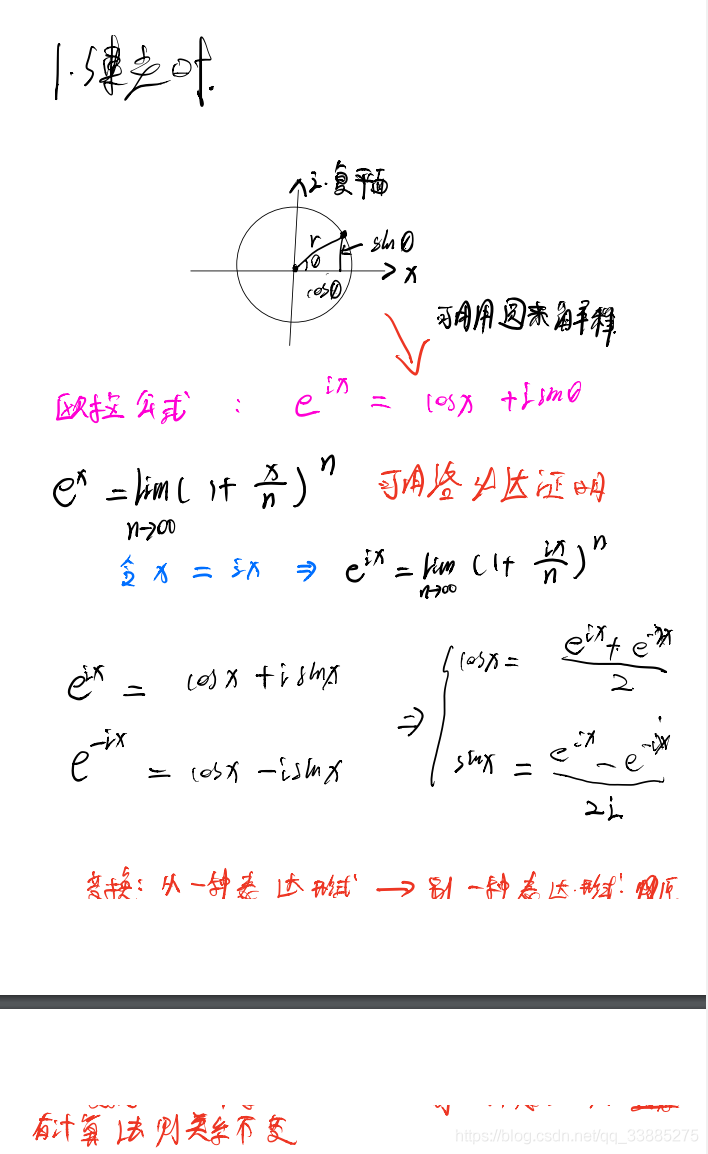
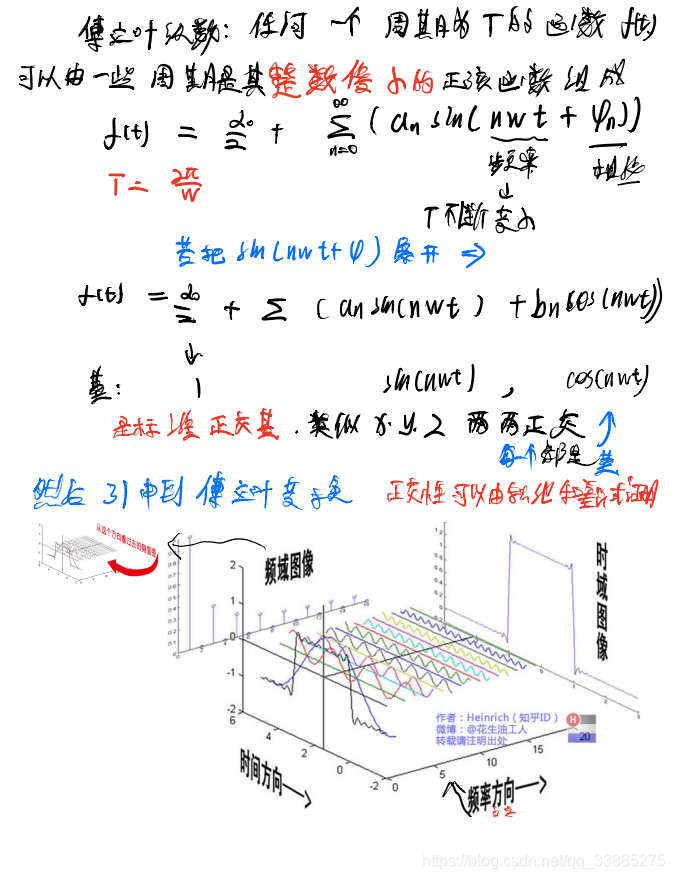
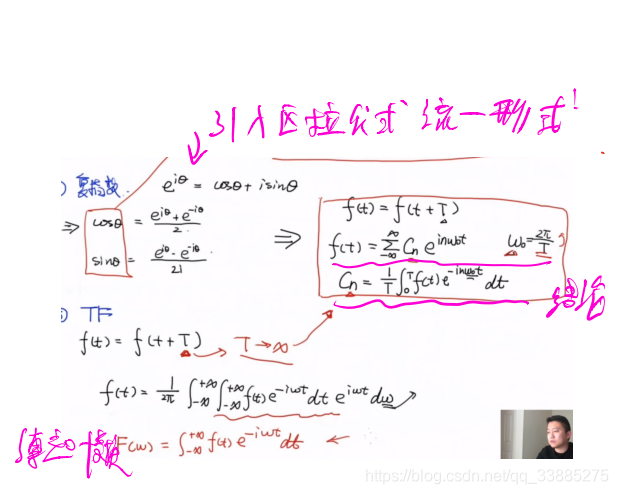
傅里叶级数
公式原型




代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
# x, y 的参数方程,用来计算在某个时间进度下,x和y的坐标
def fx(t):
x = 2 * np.cos(t) - np.cos(2*t)
return x
def fy(t):
y = 2* np.sin(t) - np.sin(2*t)
return y
def ft(t):
x = fx(t)
y = fy(t)
return x + 1j * y
t= np.linspace(0, 2 * math.pi, 100)
x = fx(t)
y = fy(t)
# 查看原始数据
plt.title('the origin data')
plt.plot(x, y, c = 'blue')
# plt.show()
# 微分计算的步长
dx = 0.001
# 计算定积分, dx是微分程度, left, right是上下界
def calF(f, dx, left, right):
Sum = 0
# 选值进行计算的点
xNum = np.linspace(left, right, int((right-left) /dx) )
for i in xNum:
now = f(i) * dx
Sum += now
return Sum
tmpf = lambda x: x**2
ans = calF(tmpf, dx, 0, 1)
print(ans)
T = 2 * math.pi
wo = 2 * math.pi / T
# 这里用得是欧拉公式化简后的 e 的指数形式
c = []
# 这里的范围就相当于是圈数
for i in range(-30, 30):
print(i)
tmpf = lambda x: ft(x)* np.exp(-1j * i * wo * x) # 隐函数表达式
nowc = calF(tmpf, dx, 0, T) / T # 定积分计算, 因为具有着正交的性质
c.append([i, nowc])
print(c)
# 计算傅里叶级数的函数
def FinallFunc(t):
Sum = 0
for n, nowc in c:
tmp = nowc * np.exp(1j * n * wo * t)
Sum += tmp
return Sum
# 进行测试, 看是否计算出来了傅里叶级数
tx = []
ty = []
for i in t:
num = FinallFunc(i)
tx0 = num.real
ty0 = num.imag
tx.append(tx0)
ty.append(ty0)
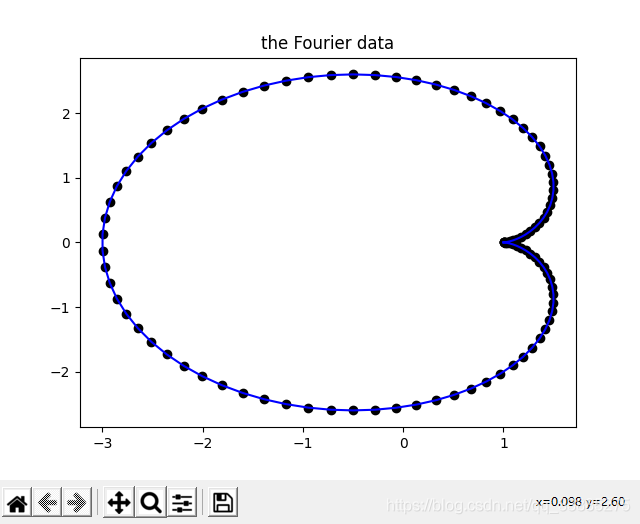
plt.title('the Fourier data')
plt.scatter(tx, ty, c= 'black')
plt.show()
|
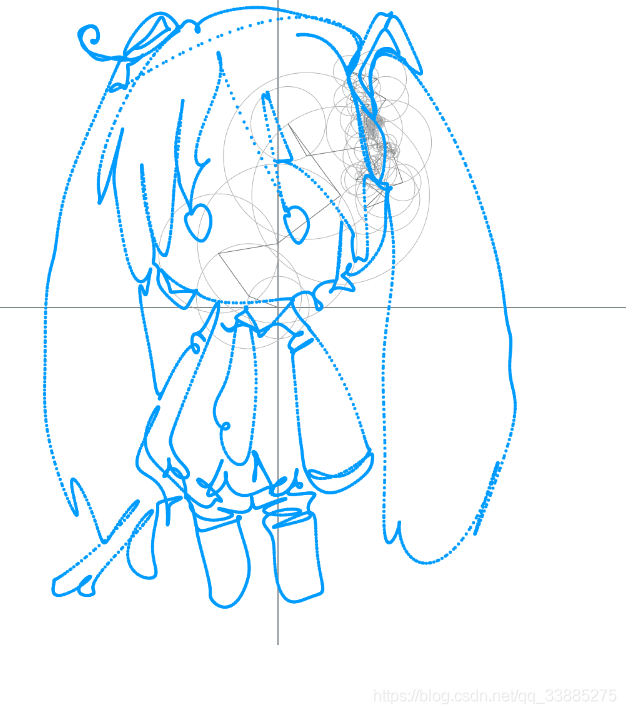
结果,拟合效果很好

数据变成离散的点,将这些点变成一个近似函数
那么需要对数据先分段拟合成一个个小段的函数,可以直接用直线。
这里参考某位大佬的做法大佬,使用贝塞尔曲线进行拟合,不过要注意函数。
我这里就不用贝塞尔了,直接用直线替代。
每一段,分必计算c(-n) 到 cn。然后相加起来,注意每一断时间。
写好加载数据变成函数的代码后。
然后与前面的拟合代码结合。
结果: 当接近500个圈的时候就效果很不错了。
 底层工程在github
底层工程在github

 底层工程在github
底层工程在github